Have you ever wondered how companies make products irresistible? Learn about the puzzle pieces that drive marketing strategies – “What Are 4P of Marketing” – and uncover the secrets behind successful brands.
In business and commerce, marketing connects products and services to those who need them, serving as the creative means to tell compelling stories, create demand, and guide consumer choices. Within this dynamic realm, the “4Ps” framework stands as a crucial guide for marketers aiming to capture customer attention and loyalty. But what exactly are these 4Ps of marketing, and why do they matter?
Think of embarking on an adventurous journey, much like a treasure hunt. Success hinges on four essential tools: a map, a compass, a flashlight, and a treasure chest. These tools mirror the 4Ps of marketing, enabling businesses to navigate the complex marketing terrain, locate their target audience, highlight their offerings, and ultimately uncover the treasure of success.
Let’s delve into these 4Ps—the essential tools that empower marketers in the dynamic business environment. We’ll explore each one to grasp its significance and understand how they synergize to craft effective marketing strategies. Discovering the 4Ps of marketing reveals their pivotal role in shaping the landscape of business and commerce.
What are the 4ps of marketing?
The 4Ps of Marketing, also known as the Marketing Mix, is a foundational framework in marketing. E. Jerome McCarthy first introduced it in the 1960s, and it remains one of the most enduring and fundamental concepts in marketing strategy.
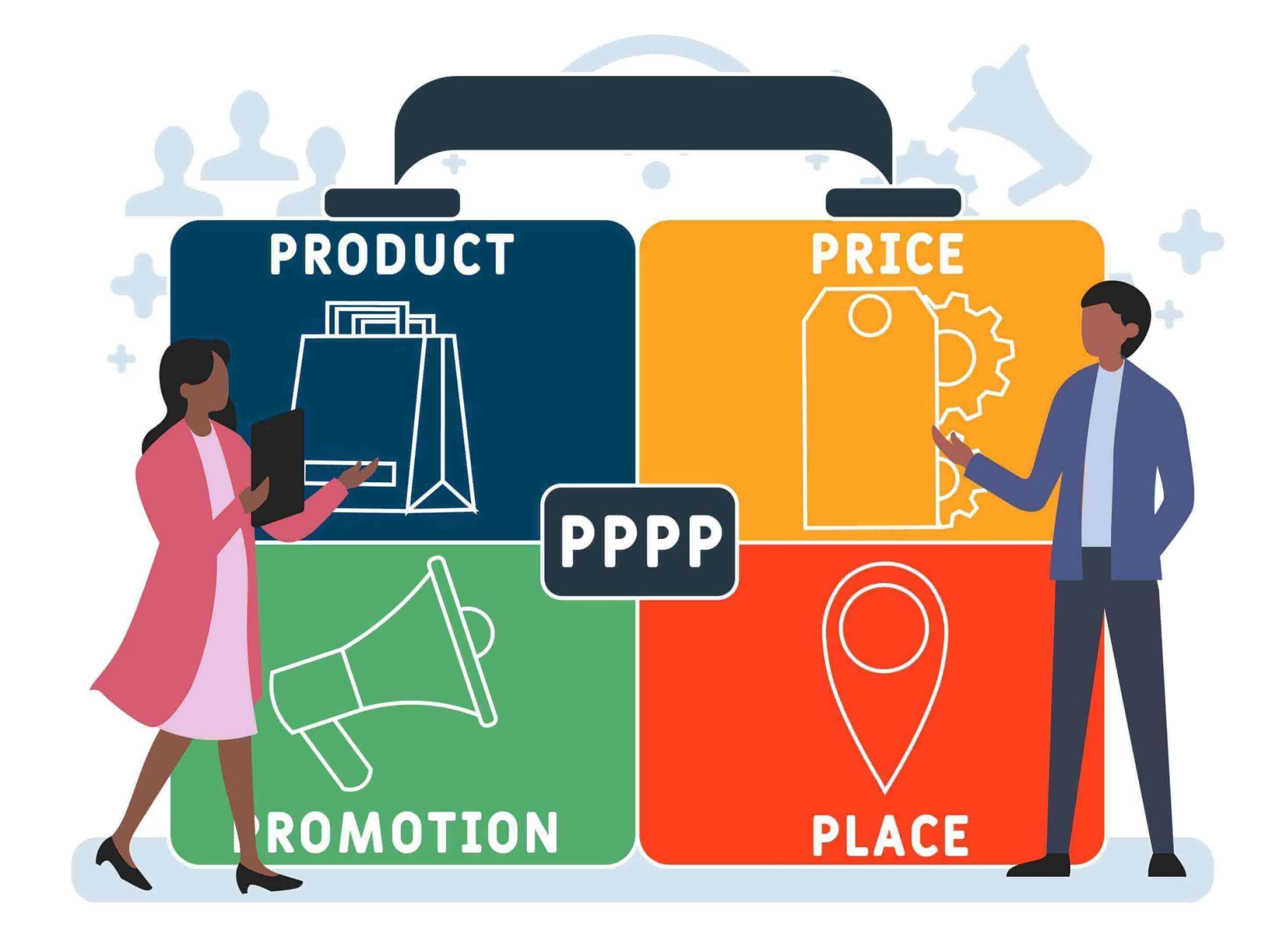
In essence, the 4Ps represent four key elements critical to any marketing strategy’s success. These elements are Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. They are the building blocks upon which a company’s marketing efforts are constructed, and when used effectively, they can help businesses achieve their goals and connect with their target audiences.
Significance of the 4Ps in marketing strategy
Understanding the significance of the 4Ps in marketing strategy is essential for any business, whether it’s a multinational corporation or a small startup. Here’s why these four elements are so crucial:
1. Comprehensive approach
2. Customer-centric
3. Competitive advantage:
4. Flexibility
5. Goal alignment
1. Comprehensive approach:
The 4Ps provide a comprehensive framework covering all marketing strategy aspects. They ensure that marketers consider all critical elements when planning their campaigns, avoiding oversights or neglecting important factors.
2. Customer-centric:
The 4Ps place the customer at the center of the marketing strategy. By considering the product, its price, where and how it’s available, and how it’s promoted, companies can tailor their offerings to meet customer needs and preferences effectively.
3. Competitive advantage:
Careful consideration and execution of the 4Ps can lead to a competitive advantage. It allows a company to differentiate its product or service from competitors, whether through pricing, unique features, or innovative promotional strategies.
4. Flexibility:
The 4Ps framework is adaptable to various industries and markets. Whether you’re marketing consumer goods, services, or even non-profit initiatives, you can apply the principles of product, price, place, and promotion to develop a winning strategy.
5. Goal alignment:
The 4Ps help align marketing efforts with business objectives. They ensure that marketing investments are directed toward activities that drive sales, enhance brand image, and ultimately contribute to the company’s success.
The Four Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion
The 4Ps of Marketing provide a structured and comprehensive approach to developing and executing marketing strategies. They empower businesses to consider every aspect of their marketing efforts, from product development to reaching and persuading customers. Understanding and leveraging the 4Ps can be a game-changer for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
- Product (Product strategy)
- Promotion (Promotional Strategy)
- Price (Pricing strategy)
- Promotion (Promotional Strategy)
Product (Product strategy)
At its core, product refers to what a business offers to meet customer needs or wants. It encompasses not only the physical item but also its features, design, quality, and any associated services. Effective product management involves understanding customer preferences, continuous improvement, and innovation to stay competitive.
The “Product” element within the 4Ps of Marketing refers to the tangible goods or intangible services a company offers to meet the needs or wants of its target market. Essentially, it’s what the customer is buying. The product element is fundamental because it sets the stage for all other marketing decisions.
For goods, a product includes not only the physical item but also its quality, design, features, and any additional attributes like warranties or customer support. For services, the product element encompasses the type of service, its quality, and any service-related features or guarantees.
Importance of product development
Product development is a critical aspect of the product element. It involves creating, enhancing, or modifying products or services to meet changing customer needs and preferences. The importance of product development lies in the following:
1. Staying competitive:
In dynamic markets, companies must continuously innovate and update their products to stay ahead of competitors. Customers often seek newer, more advanced, or more relevant solutions.
2. Meeting customer demands:
Product development allows a company to adapt to evolving customer demands and expectations. It ensures that products align with what the market desires.
3. Addressing obsolescence:
Products have a life cycle, and over time, they can become outdated or irrelevant. Effective product development helps extend a product’s lifespan or transition to newer offerings.
Key considerations in product strategy
To craft a robust product strategy, several key considerations must be taken into account:
1. Product design and features
Functionality:
The product should effectively fulfill the needs it was designed for. It should be user-friendly and reliable.
Design aesthetics:
Aesthetics can greatly influence consumer choices. An appealing design can create a competitive edge.
Innovation:
Regularly introducing new features or improvements can keep the product fresh and exciting for customers.
2. Branding and packaging
Branding:
Creating a strong brand identity is vital. A brand represents the values, personality, and reputation associated with a product. Effective branding builds trust and loyalty.
Packaging:
Packaging not only protects the product but also serves as a marketing tool. It can convey information, influence perceptions, and facilitate recognition on store shelves.
3. Product life cycle
Introduction:
The initial stage where the product is launched. Marketing efforts focus on building awareness and interest.
Growth:
Sales start to increase, and competition intensifies. Companies often invest in advertising and expanding distribution.
Maturity:
Sales stabilize, and competition peaks. Marketing may shift to focus on product differentiation.
Decline:
Sales decline due to market saturation or changing customer preferences. Companies may consider product discontinuation or replacement.
Examples of successful product strategies
1. Apple’s iPhone:
Apple’s constant innovation in design and features, along with its strong branding, has made the iPhone a global icon. Regular product updates and new features keep customers engaged.
2. Coca-Cola’s product diversification:
Coca-Cola has expanded its product line to include various beverages to cater to diverse consumer preferences. They have products like Diet Coke, Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, and an array of flavored drinks.
3. Toyota’s hybrid vehicles:
Toyota’s introduction of hybrid technology with the Prius addressed growing environmental concerns and changed the automobile industry’s landscape.
In essence, the product element of the 4Ps underscores the pivotal role that the product or service plays in marketing strategy. Companies must offer products that meet customer needs and continually innovate to remain competitive and relevant in the market. Effective product development, design, and branding are essential components of a successful product strategy.
2- Price (Pricing strategy)
Price represents the amount a customer pays for a product or service. Setting the right price is critical, as it directly impacts a company’s revenue and profitability. Pricing strategies can include cost-based approaches, competitor-based strategies, or value-based pricing, where the perceived value to the customer is a key consideration.
The “Price” element in the 4Ps of Marketing refers to the amount of money customers are willing to pay for a product or service. It’s not just a number on a price tag; it’s a strategic decision that can significantly impact a company’s success. Pricing goes beyond cost recovery; it encompasses the value perceived by customers and the competitive landscape.
Significance of pricing in marketing
Pricing holds immense significance in marketing for several reasons:
1. Revenue generation:
Pricing directly affects a company’s revenue. The right pricing strategy can maximize profits, while poor pricing decisions can lead to financial losses.
2. Customer perception:
Price influences how customers perceive a product’s quality and value. Higher prices may convey luxury or premium quality, while lower prices might signal affordability.
3. Market positioning:
Pricing is a tool for positioning a product within the market. Companies can choose to position themselves as low-cost leaders, offering the best value or as premium providers with higher prices.
4. Competitive advantage:
An effective pricing strategy can provide a competitive edge. It can deter competitors or attract customers by offering better value for the price.
Key considerations in pricing strategy
To develop a successful pricing strategy, companies must consider various factors, including:
1. Cost-based pricing vs. Value-based pricing
– Cost-based pricing:
This method involves calculating the cost of producing the product or delivering the service and adding a markup to ensure profitability. It’s straightforward but may not capture the perceived value by customers.
– Value-based pricing:
Here, the price is determined by the perceived value the product or service provides to customers. This method considers what customers are willing to pay based on benefits and satisfaction.
2. Competitive pricing strategies
– Premium pricing:
Setting a higher price to position the product as exclusive or of higher quality. Luxury brands often use this strategy.
– Penetration pricing:
Offering products at lower prices to gain market share or penetrate new markets. This strategy aims to attract price-sensitive customers.
– Skimming pricing:
Initially, setting a high price to capture early adopters or customers willing to pay a premium. Prices are gradually reduced as competition intensifies.
3. Dynamic pricing
– Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices in real-time based on various factors such as demand, time of day, customer location, or competitor pricing. It’s commonly used in e-commerce and the airline industry.
Real-world pricing strategy examples
1. Netflix subscription tiers:
Netflix offers different subscription tiers at varying price points, catering to a wide range of customers. This pricing strategy allows customers to choose the level of service and features that best suit their needs and budget.
2. Amazon’s dynamic pricing:
Amazon adjusts its prices constantly based on factors like demand and competitor pricing. This dynamic pricing strategy helps maximize revenue and profit in the highly competitive e-commerce landscape.
3. Apple’s premium pricing:
Apple positions itself as a premium brand, and its pricing reflects this. Customers associate Apple products with quality and innovation, allowing the company to maintain higher profit margins.
In summary, the price element in the 4Ps of Marketing is a multifaceted aspect of marketing strategy. It goes beyond setting a simple price tag and involves considerations of cost, value, competition, and customer perception. A well-thought-out pricing strategy can have a profound impact on a company’s success in the market.
3- Place (Distribution Strategy)
Place relates to how and where customers can access the product or service. It involves distribution channels, retail locations, online platforms, and the overall availability of the offering. An optimal place strategy ensures that the product reaches the right customers at the right time and in the right location.
In the context of the 4Ps of Marketing, the “Place” element refers to the distribution strategy, which focuses on how a company gets its products or services into the hands of customers. It’s about making the product available at the right time and in the right place to meet customer needs efficiently.
Role of Distribution in Marketing
Distribution plays a pivotal role in marketing for several reasons:
1. Accessibility:
It ensures that products are accessible to customers when and where they want them, increasing convenience and satisfaction.
2. Market coverage:
Distribution strategies determine how extensively a product is available in the market, from local to global reach.
3. Cost efficiency:
Efficient distribution can reduce costs related to storage, transportation, and inventory management.
4. Competitive advantage:
Effective distribution can give a company a competitive edge by ensuring products are available in locations or channels that competitors can’t match.
Key Considerations in distribution strategy
To create a successful distribution strategy, companies must consider various factors, including:
1. Channel selection and management
– Direct vs. indirect channels:
Companies must decide whether to sell directly to consumers or use intermediaries like retailers, wholesalers, or distributors.
– Channel partnerships:
Building strong relationships with channel partners is crucial for successful distribution. Effective communication and collaboration are key.
2. Retail vs. E-commerce distribution
– Retail distribution:
Traditional retail involves selling products through physical stores. It’s still relevant, especially for certain product categories and demographics.
– E-commerce distribution:
The rise of online shopping has led to the growth of e-commerce distribution. Companies must optimize their online presence, user experience, and logistics for e-commerce success.
3. Supply chain optimization
– Inventory management:
Efficient management of inventory ensures products are available when needed without excessive carrying costs.
– Logistics and transportation:
Choosing the right transportation methods and partners is critical for timely and cost-effective distribution.
Case studies of effective distribution strategies
1. Amazon’s fulfillment network:
Amazon has built one of the most extensive and efficient distribution networks globally. Their use of advanced technology and strategically located fulfillment centers ensures quick and reliable product delivery, contributing to their dominance in e-commerce.
2. Coca-Cola’s global reach:
Coca-Cola’s beverages are available in nearly every corner of the world, thanks to a well-established distribution network that includes partnerships with bottlers, distributors, and retailers. This extensive distribution has contributed to its status as a global brand.
3. Zara’s fast fashion model:
Zara’s distribution strategy revolves around fast fashion. They use a just-in-time manufacturing and distribution system that allows them to respond quickly to changing fashion trends and get new products into stores at record speed, attracting fashion-conscious customers.
In conclusion, the place element, or distribution strategy, is a crucial aspect of marketing. It ensures products are available where and when customers want them, contributing to customer satisfaction and a company’s competitive advantage. Effective distribution requires careful planning, channel selection, and supply chain optimization, as demonstrated by successful companies across various industries.
4- Promotion (Promotional Strategy)
In the realm of the 4Ps of Marketing, the “Promotion” element represents the strategies and activities used to communicate and promote a product or service to the target audience. It’s about spreading the word and persuading customers to choose a particular product or service over competitors.
Importance of promotional activities
Promotional activities are of paramount importance in marketing for several compelling reasons:
1. Awareness and visibility:
Promotion creates awareness about a product or service, ensuring that potential customers know it exists.
2. Brand building:
Consistent and effective promotion helps build and reinforce a brand’s image, values, and identity in the minds of consumers.
3. Persuasion:
Promotional efforts are designed to persuade customers to make a purchase. They highlight the unique selling points and benefits of a product or service.
4. Customer engagement:
Promotion is a tool for engaging with customers, gathering feedback, and maintaining a relationship with them.
Key considerations in promotional strategy
Crafting a successful promotional strategy entails considering several key factors:
1. Advertising and marketing communication
– Media Selection:
Choosing the right advertising channels, such as TV, radio, print, online, or social media, depends on the target audience and budget.
– Message Development:
Crafting compelling and clear messages that resonate with the target audience is essential. Messages should highlight the product’s benefits and how it solves customer problems.
– Timing:
Timing plays a critical role in advertising. Launching campaigns at the right time can coincide with consumer needs and trends.
2. Sales promotion and public relations
– Sales promotion:
This includes activities like discounts, coupons, contests, and special offers aimed at stimulating immediate sales. It can be particularly effective for attracting price-sensitive customers.
– Public relations:
Building a positive public image through media coverage, community engagement, and crisis management is crucial. Strong PR can enhance credibility and trust.
3. Digital marketing and social media
– Digital marketing:
In today’s digital age, online marketing, including pay-per-click advertising, email marketing, and content marketing, is essential for reaching a broad and targeted audience.
– Social media:
Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter allow companies to connect with customers, share content, and engage in direct conversations. Social media is a powerful tool for building brand loyalty.
D. Notable promotional campaigns
1. Nike’s “Just Do It”:
Nike’s iconic slogan has become synonymous with the brand. This simple yet powerful phrase, combined with impactful advertising featuring athletes, has contributed to Nike’s global success.
2. Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke”:
Coca-Cola’s campaign involved personalizing its soda cans and bottles with common first names. This approach created a personal connection with customers and encouraged social sharing.
3. Dove’s “Real Beauty”:
Dove’s campaign challenged traditional beauty standards by featuring real women of all shapes and sizes. It sent a powerful message about self-esteem and body positivity.
In summary, the promotion element in the 4Ps of Marketing is a critical aspect of marketing strategy. It involves communicating the value of a product or service to the target audience through various means, including advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and digital marketing. Effective promotional strategies can shape customer perceptions and drive purchasing decisions, as demonstrated by these notable campaigns.
Integration of the 4Ps
In the world of marketing, the concept of the “4Ps” has long been a fundamental framework for understanding and executing marketing strategies. These four pillars—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—have guided marketers in shaping their campaigns and reaching their target audiences effectively. However, in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the integration of these 4Ps has become more crucial than ever.
In this section, we will delve into integrating the 4Ps and explore how this approach can lead to more holistic and successful marketing initiatives.
- Interdependence of the four Ps
- Creating a holistic marketing mix
- Balancing the 4Ps for maximum impact
Interdependence of the four Ps
The success of a marketing strategy lies in the harmonious interdependence of the four Ps: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. These elements are not silos but rather intricately connected components that influence and rely on each other.
For example, the product’s features and quality significantly impact its pricing. A premium product typically commands a higher price, while a budget-friendly product may require cost-efficient production. Similarly, the choice of distribution channels (Place) can affect the product’s accessibility to the target market and thus influence its pricing and promotional strategy.
Creating a holistic marketing mix
A holistic marketing mix is about creating a seamless blend of the four Ps that aligns with the overall business objectives and meets customer needs. Here’s how they can be integrated cohesively:
1. Product-price integration:
The product’s design, features, and quality should justify its price. Pricing should consider the costs involved in creating the product and delivering it to customers.
2. Product-place integration:
The distribution channels should align with the product’s nature and target market. For example, premium products may be best suited for exclusive retail locations, while everyday items may thrive in a variety of retail and online channels.
3. Product-promotion integration:
Promotion should highlight the product’s unique selling points and benefits. The message should resonate with the target audience and be consistent with the product’s branding.
4. Price-place integration:
The distribution strategy should consider pricing, ensuring that the cost of distribution doesn’t significantly eat into profit margins. Efficient distribution can sometimes lead to cost savings that can be passed on to customers.
5. Price-promotion integration:
Promotional activities, such as discounts or sales promotions, should align with the pricing strategy. Discounts should make sense in the context of the product’s price.
6. Place-promotion integration:
Promotion should create awareness of where and how customers can access the product. For instance, if a product is available online, digital marketing and social media promotion can effectively reach the target audience.
Balancing the 4Ps for maximum impact
Balancing the four Ps is a delicate art that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Achieving this equilibrium ensures that a marketing strategy is not lopsided, where one element overwhelms the others, but rather a symphony where each element harmonizes with the rest.
– Product-centric balance:
In some cases, like new product launches, the focus may be on the product itself. However, it’s essential to consider how pricing, distribution, and promotion support the product’s success.
– Customer-centric balance:
Ultimately, the balance should be customer-centric. All four Ps should align with customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. This customer-centric approach ensures that the marketing mix resonates with the target audience.
– Continuous monitoring:
Markets change, customer preferences evolve, and competitors adapt. Regularly assessing the performance of the four Ps and making necessary adjustments is vital for maintaining balance and relevance.
In conclusion, the integration of the four Ps in marketing is akin to orchestrating a symphony where each instrument plays a crucial role. Balancing the product, price, place, and promotion elements ensures that a marketing strategy is cohesive, customer-focused, and maximally impactful. It’s a dynamic process that requires careful consideration and ongoing adjustment to stay in tune with changing market dynamics.
Why businesses should continuously refine their marketing
As we move forward in a dynamic and competitive business environment, businesses are encouraged to view the 4Ps not as static principles but as a dynamic marketing mix that requires continuous refinement. Here’s why:
1. Changing consumer behavior
2. Technological advancements
3. Globalization
4. Environmental and ethical concerns
5. Competitive landscape
1. Changing consumer behavior:
Consumer preferences, needs, and behaviors evolve. To stay relevant, businesses must periodically assess whether their product, price, place, and promotion strategies align with these changes.
2. Technological advancements:
Technology continually reshapes how products are developed, priced, promoted, and distributed. Staying abreast of these technological advances and incorporating them into the marketing mix can provide a competitive edge.
3. Globalization:
In a global economy, businesses must consider how their marketing mix adapts to different cultures, regulations, and economic conditions around the world.
4. Environmental and ethical concerns:
Increasingly, consumers are concerned about the environmental and ethical implications of the products they buy. Adjusting the product and promotional elements to address these concerns can be advantageous.
5. Competitive landscape:
Rivals are constantly innovating. Stagnation can lead to market share loss. Regularly evaluating and adjusting the 4Ps can help businesses maintain or gain a competitive advantage.
In conclusion, the 4Ps of Marketing are more than a historical framework; they are a compass for modern marketing strategy. Businesses that embrace their enduring relevance and commit to the ongoing refinement of their marketing mix are better positioned to thrive in a rapidly changing business landscape. The 4Ps provide a solid foundation for businesses to build innovative and effective marketing strategies that resonate with today’s consumers.
Conclusion
The 4Ps of Marketing—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—remain as relevant today as when they were first introduced. These foundational elements guide successful marketing strategies despite the evolving business and marketing landscape.
The enduring relevance of the 4Ps lies in their adaptability. They provide a framework that can be applied across diverse industries, markets, and consumer behaviors. Whether you’re marketing consumer goods, services, or innovative tech products, the 4Ps serve as a compass to navigate the complex marketing world.
Moreover, in an era dominated by digital technology and data-driven insights, the 4Ps have proven adaptable. They seamlessly integrate with modern marketing techniques, from e-commerce to social media advertising, allowing businesses to harness new tools while maintaining a solid foundation.
- “As chicaadmin at The Chicago Weekly, I curate trending national and international news stories with a focus on social justice and cultural impact. My passion for journalism and commitment to independent media are fueled by my Chicago roots and belief in the power of storytelling to connect communities. Follow me on Twitter for insightful commentary and news updates!”